Climate change is one of the most significant environmental challenges facing the world today. Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and land-use changes, are the primary cause of global warming. To mitigate the effects of climate change, reducing carbon dioxide emissions is essential. However, reducing emissions alone is not enough; we must also find ways to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Enhanced Mineral Weathering (EMW) is a promising solution that has gained significant attention in recent years.
What is Enhanced Mineral Weathering?
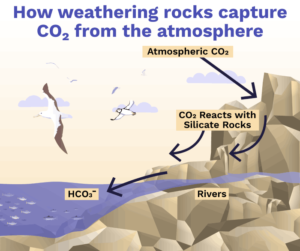 Enhanced Mineral Weathering is a natural process that involves accelerating the reaction between rocks and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Normally the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere reacts with the rocks, forming bicarbonate ions. These bicarbonate ions are carried by water to the ocean, where they form a stable mineral, such as calcium carbonate (limestone). The adsorption occur naturally when the gas reacts with silicate rocks, but the process is slow, taking thousands of years. EMW involves adding ground-up rock, such as basalt or olivine, to soils or spreading it over land surfaces to accelerate the process.
Enhanced Mineral Weathering is a natural process that involves accelerating the reaction between rocks and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Normally the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere reacts with the rocks, forming bicarbonate ions. These bicarbonate ions are carried by water to the ocean, where they form a stable mineral, such as calcium carbonate (limestone). The adsorption occur naturally when the gas reacts with silicate rocks, but the process is slow, taking thousands of years. EMW involves adding ground-up rock, such as basalt or olivine, to soils or spreading it over land surfaces to accelerate the process.
Different Techniques of EMW
There are several techniques used to enhance mineral weathering such as In-situ EMW where ground-up rock is applied to the soil directly, either through spreading or injection. This method is relatively simple and does not require significant changes to agricultural practices. Co-deposition is a method that involves adding ground-up rock to the ocean floor, where it reacts with carbon dioxide to form stable minerals.

This method has the potential to store large amounts of carbon dioxide in the deep ocean over a long period. Another method is Alkaline paper mill waste: Alkaline paper mill waste contains calcium and magnesium silicate minerals that can react with carbon dioxide to form stable minerals. The waste is applied to agricultural soils, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and enhancing carbon sequestration.
Funding for this kind of technologies has increased exponentially in recent years from both private and public. The different methodologies and implementation of EMW contributed to the birth of a variety of ventures such as CarbFix, a carbon capture and storage project that utilizes enhanced mineral weathering to capture and store carbon dioxide. The project is located in Iceland and is a collaboration between the University of Iceland, Columbia University, and Reykjavik Energy. The CarbFix project captures carbon dioxide from a nearby geothermal power plant and injects it into basalt formations deep underground. The carbon dioxide reacts with the basalt, forming stable minerals such as calcium carbonate. The project has been successful in capturing and storing carbon dioxide, and the injected carbon dioxide has mineralized into stable minerals in less than two years.

Another interesting venture is Project Vesta which utilizes enhanced mineral weathering to capture and store carbon dioxide. The project involves adding finely ground olivine to beaches, where it reacts with carbon dioxide in the seawater and forms stable minerals such as magnesium carbonate. The project aims to mitigate ocean acidification and sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The Project Vesta has been successful in reducing the acidity of seawater and promoting the growth of marine organisms such as corals and shellfish.
Based on a similar principle, PrimLab, an R&D lab based in Spain developed and patented CO2Pure, a mineral-based compound able  to adsorb and mineralize CO2, NOx and volatile organic compounds (VOC) into unharmful carbonates such as calcium and magnesium carbonates, thanks to the processes of photocatalysis (chemical reaction through light) and catalysis. The compound has already been through the testing and certification phases from a series of research institutes, universities and certification bodies. CO2Pure can be used by itself or implemented as an additive on multiples surfaces, hence its number of applications its quite extensive: from roads to paints, plastics, rubbers and textiles, to name few.
to adsorb and mineralize CO2, NOx and volatile organic compounds (VOC) into unharmful carbonates such as calcium and magnesium carbonates, thanks to the processes of photocatalysis (chemical reaction through light) and catalysis. The compound has already been through the testing and certification phases from a series of research institutes, universities and certification bodies. CO2Pure can be used by itself or implemented as an additive on multiples surfaces, hence its number of applications its quite extensive: from roads to paints, plastics, rubbers and textiles, to name few.
Pros & Cons of EMW
Since we are all concerned about climate change, one of the advantages of EMW is carbon sequestration with the potential to capture large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in the earth’s crust, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change. At the same time in can improve the soil quality by providing essential nutrients and increasing the soil’s pH.It is a cost-effective and relatively low-cost solution compared to other carbon capture and storage technologies while at the same time being widely applicable: EMW can be applied to a range of land uses, including agriculture, forestry, and land restoration projects.
Grinding the rocks into a fine powder and applying them to the soil may require mining the rocks and consume significant amounts of energy and resources, which could negatively offset the carbon capture benefits. While this can be tracked and calculated, a major difficulty in the implementation of EMW methodologies are the monitoring and the measuring of the results: EMW requires long-term monitoring to ensure that the carbon dioxide is being sequestered effectively and to identify any potential environmental risks. We have been discussing measuring, reporting and verification (MRV) in a previous article, the importance of which is exponentially increasing, in parallel with the development of new methodologies of carbon absorption and sequestration.
Conclusion
Enhanced Mineral Weathering is a promising solution to the problem of carbon dioxide emissions and climate change. It has the potential to capture significant amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in the earth’s crust, providing a long-term solution to greenhouse gas emissions. While there are some limitations, such as the performance monitoring and the energy required to grind them, the advantages outweigh the disadvantages. With further research & development, it can be another valuable instrument to reach the climate targets the planet so desperately need.